BIM Integration: Why It Matters to Manufacturers
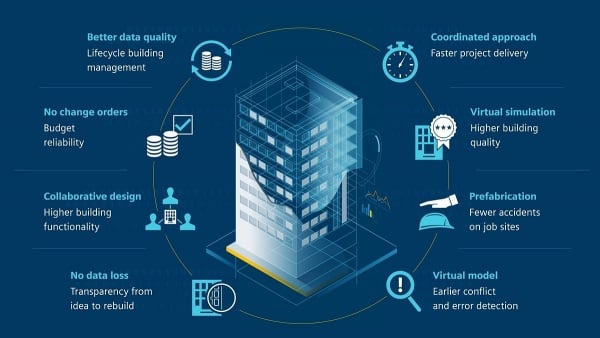
Building information management (BIM) is a collaborative process for ensuring that planning, design and construction are as efficient and collaborative as possible, especially for manufacturing or commercial facilities. BIM is also evolving rapidly, due largely to new software tools such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). BIM can create virtual plans that show how all the different building components relate to each other in great detail, including the equipment on the plant floor. Such models make it easier for architects, engineers, general contractors, subcontractors and customers to evaluate the performance of different materials and systems both before and during the building process, thereby improving quality and workflow and reducing the number of change orders.

One of the most popular BIM collaboration programs is Autodesk BIM 360, which provides a variety of tools for analyzing project data and connecting teams in real time to make quick, informed decisions during the construction process. When used effectively, BIM can significantly reduce overall engineering and construction costs and shorten the timeline for the project.
Benefits of BIM
BIM enables project stakeholders to collaborate on the planning, design and construction of a manufacturing facility by interacting with one highly detailed 3D model. The data allows the construction team to make better-informed decisions during construction, often in real time, using information from the BIM model. BIM can be used during every stage of the project, from initial design through completion and even beyond (facilities management).
Benefits of BIM include:
- Improved building design. Detailed models and sophisticated calculations allow engineers to create more innovative designs which improve production and workflow. BIM can also integrate with new technologies such as 3D printing, allowing expanded design options.
- Accurate pricing. More accurate budgets and better decision-making result when highly precise BIM drawings are used to eliminate potential problems and estimate operational costs. BIM also ensures the building conforms to all code requirements.
- Efficiency. By identifying and correcting potential problems in pre-construction, BIM reduces the amount of rework, including changes made in the field such as clash detection. The result is a smoother construction operation with minimal downtime.
- Building performance and sustainability. Engineers can evaluate a building’s energy footprint with BIM and analyze the benefits of green technologies, including alternative energy sources. BIM can also determine the best systems for the operation and maintenance of the manufacturing facility post-construction.
- Safety. BIM helps identify and eliminate potential hazards and risks during construction, both in the planning phase and on-site. “Through visual models, workers can prepare and understand the entire area to mitigate risks,” states Allison Huffman, industry initiative marketing manager for Autodesk. “When potential injuries and lives are at stake, this is the ultimate bottom line that any construction team wants to achieve.”
Cloud-Based BIM
The latest BIM advancements utilize AR and VR to create sophisticated construction models that can be viewed simultaneously by different team members at different locations.
 Credit: Siemens Smart Infrastructure
Credit: Siemens Smart Infrastructure
“VR is being used for employee training and facility process layouts,” says Robert Lownes, manager of BIM/VDC at Gray. “Gray recently worked with a customer’s engineering team to use VR to walk through the project and understand the facility process. The customer’s team included process engineers in international locations. VR was the perfect way to send a file where everyone’s input was combined into one model. This was highly useful for ongoing collaboration during the project. The model will also be used to train current employees and future hires on how the facility operates.”
BIM can also be integrated with 3D printing—for example, making prototypes of building components and prefab materials for the team to consider (or creating actual production-ready building parts). It can also serve as the unified platform for Internet of Things applications on the construction site. These and other advanced capabilities, especially cloud-based programs and improved mixed reality and software tools, will further expand the many ways BIM can be used to improve the design, engineering and construction of manufacturing facilities or other industrial buildings.
- Category:
- Industry
- Opinion
- Construction
- Design
- BIM/VDC
Some opinions expressed in this article may be those of a contributing author and not necessarily Gray.
Related News & Insights
Distribution, Construction
Full Throttle: Making distribution faster than ever before
GrayWay, Industry
Manufacturing, Construction
Top Reasons to Hire a Self-Perform Contractor
Industry
Construction
Gray Honored with Rockwell Automation EPC Partner Innovation Award
Corporate News
March 26, 2024